Solutions

Digihua : Smart Manufacturing Execution System
Intel Market Ready SolutionDescription
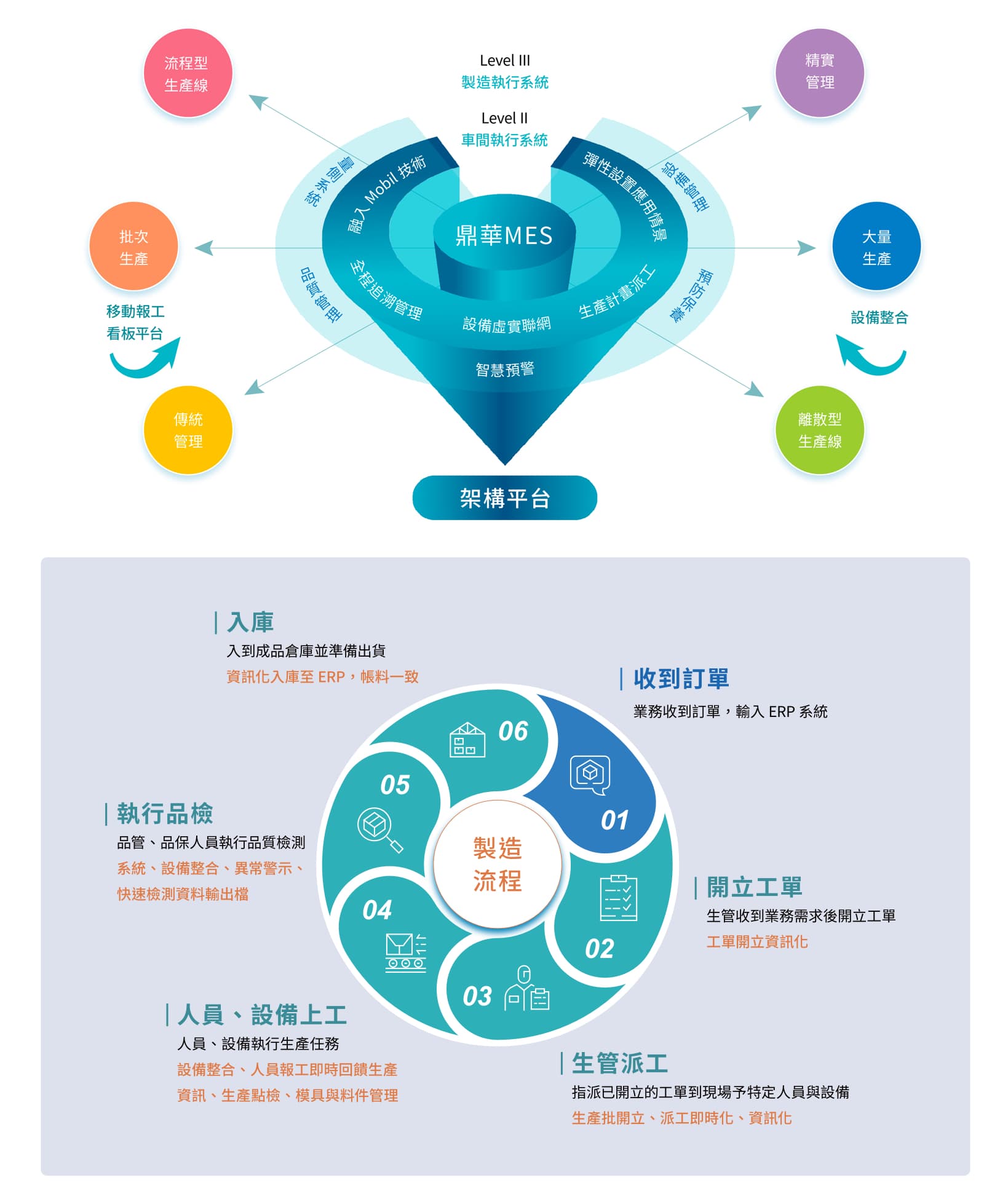
Smart Manufacturing Execution SystemThe goal is to build an intelligent factory with lean production as the objective, using time management as a competitive advantage. The production tasks are the core, and the barriers between production management and production execution are broken down to construct a closed loop of full value chain data.
Focusing on the integration of human, machine, material, method and Testing
A comprehensive analysis of pain points in production workshop management.
Human Pain Points:
- Low equipment utilization:
The lack of basic operational skills among personnel can lead to equipment failures, workpiece damage, etc., resulting in decreased equipment utilization and increased operating costs.
- Low yield:
Insufficient operational skills among personnel can lead to a decrease in product quality and yield.
- Lack of knowledge accumulation:
The inability to convert personnel work hours into experience data makes it difficult to obtain objective data and establish an internal education and training mechanism within the company.
- Disordered human resources:
Production line supervisors are unable to determine whether operational personnel have the ability to operate equipment, resulting in incorrect assignment and scheduling of personnel and wasting human resources.
Machine Pain Points:
- Lack of standardization:
The lack of a standardized maintenance plan for equipment leads to inconsistent maintenance methods and frequencies, increasing the probability of equipment failures and reducing equipment utilization and production efficiency.
- Disorganized spare parts records:
The maintenance spare parts are not recorded and managed properly.
- Chaotic paper-based historical data:
The paper-based records of historical data are disorganized and difficult to quickly access, making it hard to check the equipment's maintenance plan and records.
- Lack of analysis reports:
Unable to estimate maintenance efficiency and provide real-time feedback on maintenance status.
- No maintenance schedule:
Unable to schedule equipment maintenance based on production quantity, time, and frequency.
Material Pain Points:
- Incorrect use of materials:
The use of incorrect components and materials leads to a decrease in product quality and yield, wastes time on troubleshooting, and increases operational and time costs.
- Frequent downtime due to waiting for materials:
Inability to supply materials in a timely manner leads to a chain reaction in demand, causing delayed supply and affecting overall equipment utilization efficiency.
- Inconsistent material inventory:
Failure to report and update inventory in a timely manner leads to inconsistent material inventory, which affects procurement and production management decision-making efficiency and increases rework.
Process Pain Points:
High variability in production process changes and requirements for flexible production adjustments during processing, such as changes in processing technology or equipment, can cause frequent abnormal handling, leading to missing or additional orders due to overlooked information.
Testing Pain Points:
- Paper-based records:
Testing data and measurement records are recorded on paper, making it inefficient to search and easy to modify, which results in unreliable data.
- Inconsistent standards:
Inspecting testing standards using traditional instruments often produces inconsistent results due to human factors, making it difficult to standardize.
- Delayed abnormal alerts:
Data must be organized before abnormal alerts can be identified, and it can only be done through phone calls or email notifications.
- Difficult data analysis:
Manual data consolidation generates related reports that are difficult to search and consolidate.
- Non-transparent inspections:
Unable to know the test results in real-time.
IoT Solution Application
The core function of the sMES product is to enable interconnectivity between "human, machine, material, method, and testing"
- Personnel management includes:
Various roles or positions in the production site, such as factory managers, section chiefs, production management personnel, dispatching supervisors, equipment operators, process quality control personnel, and equipment or mold maintenance personnel.
- Equipment management includes:
Machine equipment capacity, equipment checklist, equipment maintenance, machine utilization classification analysis, equipment failure, maintenance, and mold tool life and failure management, etc.
- Material management includes:
The basic properties, production process, and quality risk warning standards of finished products, semi-finished products, and critical materials.
- Process management refers to production methods, including:
Equipment dispatch management methods, operation station in/out management methods, product process management, rework management, batch management, unit quantity conversion between processes or operation stations, and product component serial number rules, etc.
- Testing management includes:
Input and warning management of in-house QC data, which can be seamlessly integrated into the Dinghua Smart Quality Management System (sQMS) for more detailed inspection data chart analysis and tracking and prevention mechanisms for potential quality abnormalities.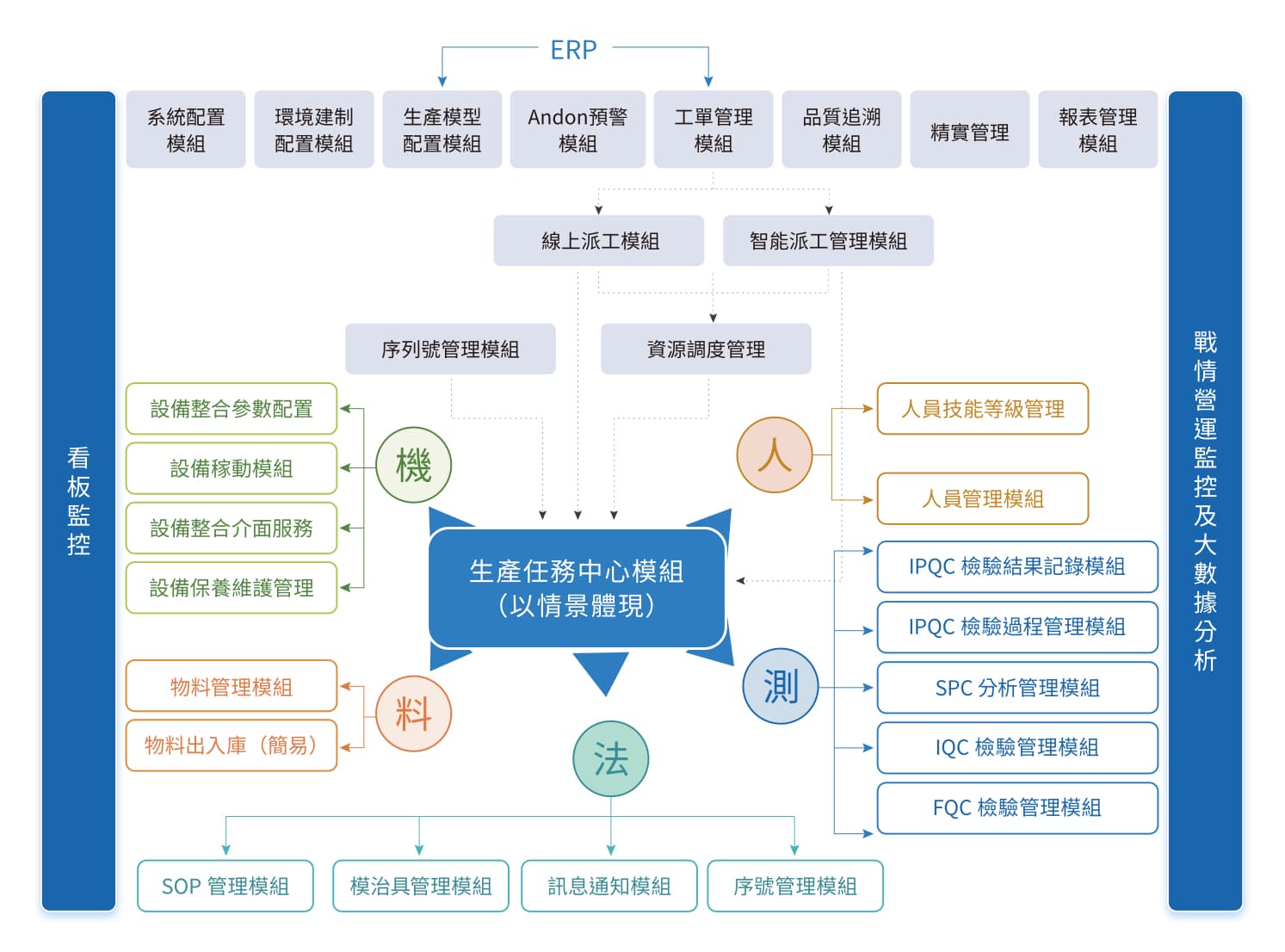
IoT Solution Specification
The four main features of sMES can help companies build a digital factory:
Feature 1:
Integration of Production and Enterprise Operation
sMES integrates various ERP systems through standard scenario coupling, including Digiwin's own ERP, Oracle, SAP, Yonyou, and Kingdee. By switching corresponding interfaces in real-time, information is not lost. The integrated content includes work orders, production data, work order materials, outsourced returns, and inventory, which allow for the reconciliation of data between the production system and the operation system. This results in more transparent product cost, progress, and history, as well as more accurate inventory quantity. It further facilitates analysis of the company's operational status from different perspectives, thereby expanding profits and maintaining advantages.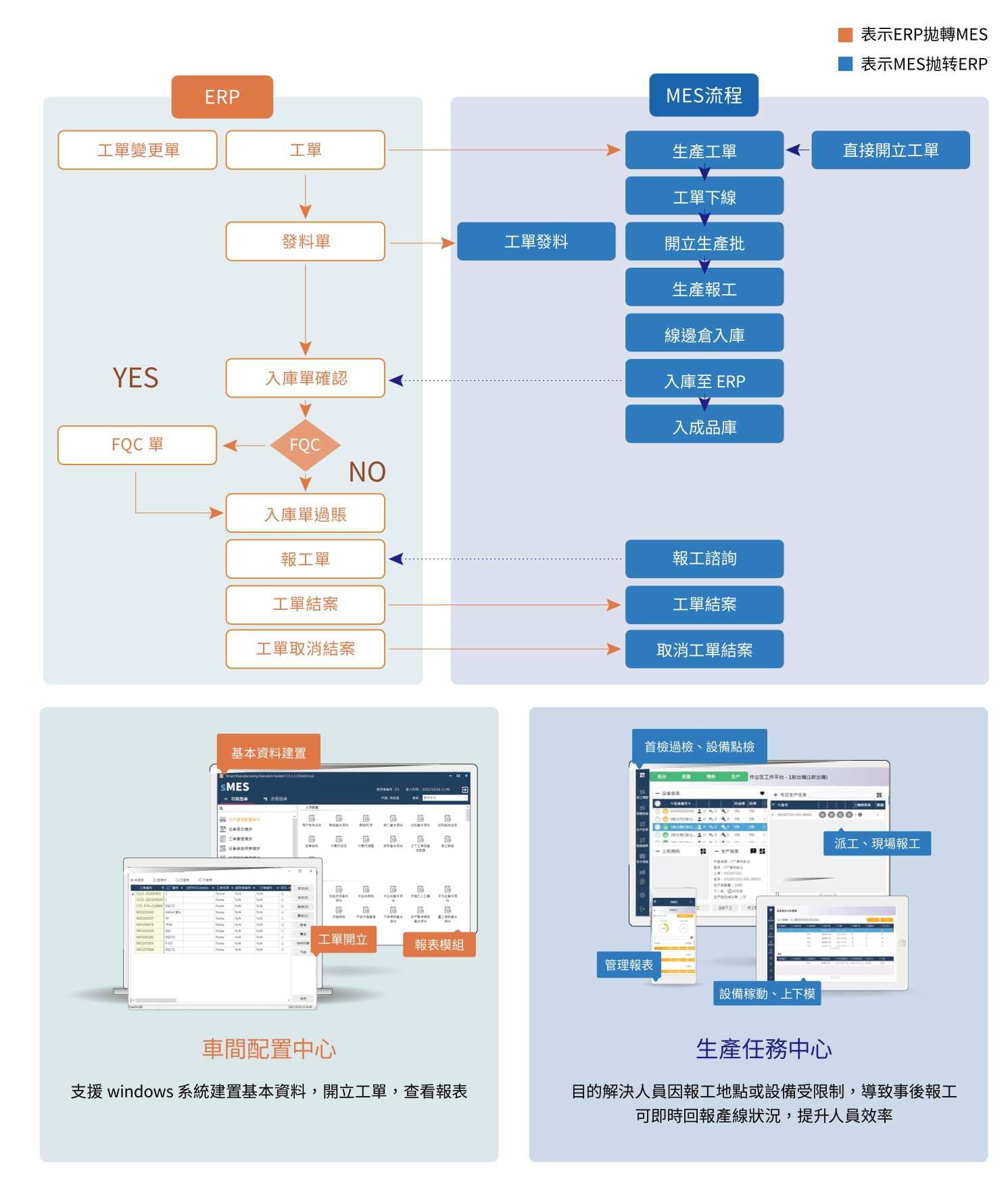
Feature 2: Flexible Configuration of Process Flow
By using a more intuitive and flexible process configuration, sMES enables flexible and agile production in various factory areas. It can support different products or changes in the production process that require the quick replacement or addition of processes. This results in a low-code and easily configurable production execution system.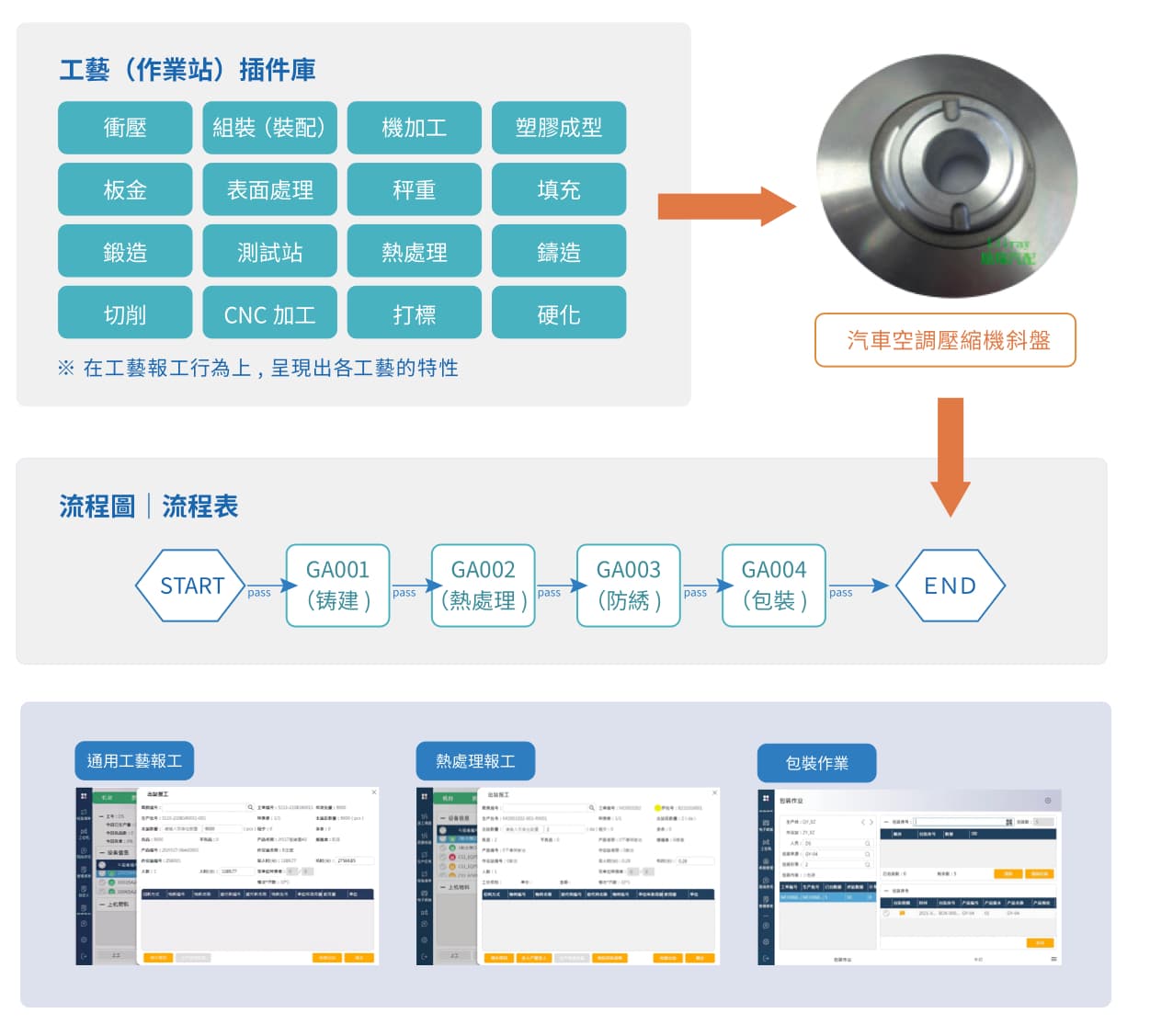
Feature 3:
Integration of IT and OT to achieve modernization of industrial network architecture
To meet the trend of the Internet of Things (IoT), a unified gateway for integrating operational technology (OT) data is provided, utilizing cross-domain technologies to integrate IT and OT data through configuration. In addition to achieving the transformation, cleaning, and traceability of OT data, this integration also enables the practical application of scenarios that merge both IT and OT data.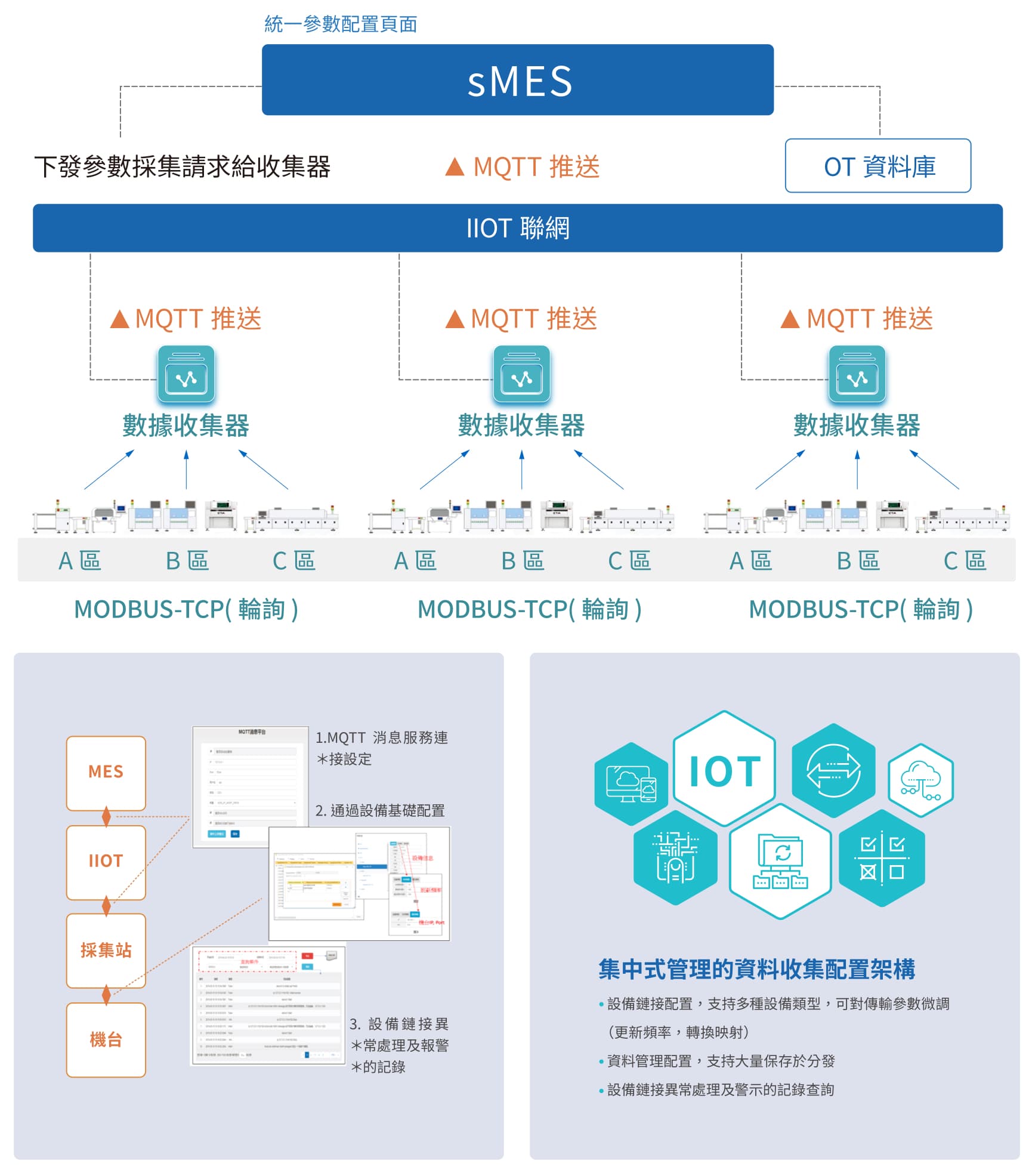
Feature 4.
Comprehensive creation of a visualized, transparent, and traceable production workshop.
MES meets the key requirements of enterprises in product management, quality control, equipment integration and management, problem tracing and analysis, and real-time data collection in the production workshop. It provides a complete blueprint for the implementation of an intelligent workshop solution. Enterprises can integrate their information requirements in stages according to industry characteristics, management methods, or production models.